Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Diabetic Neuropathy refers to nerve damage caused by Diabetes. When it affects the hands, legs and feet, it is known as Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy.
There are three different groups of nerves that can be affected by Diabetic Neuropathy:
- sensory nerves, which enable you to feel pain, temperature, vibration, pressure and other sensations
- motor nerves, which control your muscles and give them their strength and tone
- autonomic nerves, which allow your body to perform certain involuntary functions, such as sweating
Many people develop Peripheral Neuropathy long before their Diabetes is diagnosed, but are unaware of the nerve damage in their feet. The resulting loss of sensation means minor skin injuries like blisters, corns, callus, heel cracks and ingrown toenails can remain unnoticed until they develop into ulcers, which can be very difficult to heal and may require hospitalisation.
In serious cases, ulcers resulting from Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy can become gangrenous, and may lead to in amputation, disability and, in some cases, loss of life.
How is Peripheral Neuropathy different from Peripheral Arterial Disease?
Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy differs from Peripheral Arterial Disease in that the latter affects the blood vessels and circulation, whereas Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy affects the nerves.

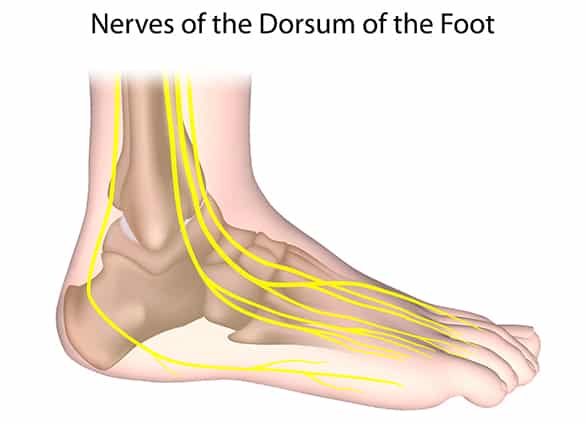
How does Diabetes lead to Peripheral Neuropathy?
High blood sugar levels cause damage to both your large blood vessels (macrovascular disease) and to your small blood vessels or capillaries (microvascular disease). Your small blood vessels supply blood to the nerves in your feet and legs, the retina in your eyes, and your kidneys. If your small blood vessels are damaged, you may develop peripheral neuropathy, diabetic retinopathy (eye disease) and nephropathy (kidney disease).
How do I know if I am at risk of developing Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy?
Anyone with Diabetes is at risk of developing Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy , but the risks increase with:
- the duration of Diabetes
- high blood sugar levels
- low insulin levels
- high blood fat levels
- blood vessel damage resulting from Peripheral Arterial Disease
- auto-immune factors affecting the nerves
- lifestyle factors such as smoking, alcohol use and lack of physical activity
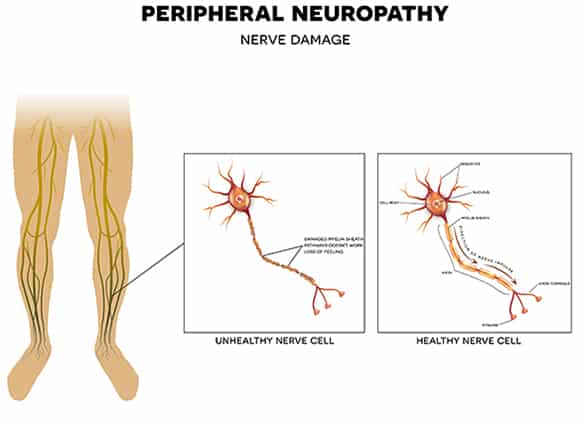

What are the warning signs of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy?
Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy develops slowly and worsens over time. It often has no symptoms, because the lack of protective sensation means many people are unable to adequately feel pain or discomfort in their feet.
Other people may experience various symptoms depending on the types of nerves involved.
Symptoms of Sensory Neuropathy are often more noticeable at night, and may include:
- numbness, pins-and-needles or tingling in the toes and feet
- a sensation of the feet being frozen, thawing, stuck to cardboard or wearing an elastic band
- pain or discomfort in the feet or legs, including sharp, burning, stabbing pain
Symptoms of Motor Neuropathy may include:
- muscle weakness and loss of muscle tone in the feet and lower legs
- poor balance or foot drop
- changes in foot shape such as flat or high arched feet, hammer toes, claw toes, or bunions.
- These foot deformities can lead to areas of increased pressure beneath the feet, resulting in ulceration
Symptoms of Autonomic Neuropathy may include:
- a diminished ability to produce adequate sweat on the skin, resulting in dry skin on the feet, heel fissures and cracks.
How is Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy diagnosed?
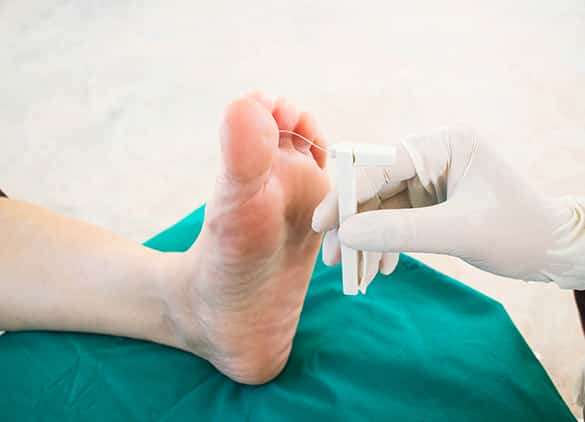
If you have diabetes, you should have a comprehensive diabetic foot assessment at least once a year. As part of this assessment, your podiatrist will conduct some simple neurological tests to determine if there is any nerve damage in your feet.
In particular, your podiatrist will test:
- your ability to feel vibration on your feet using a tuning fork or a biothesiometer
- your ability to feel pressure on the skin beneath your feet using a finely calibrated monofilament
- your ankle and knee reflexes
- the strength of the small muscles within your feet
Your podiatrist will also conduct a visual gait analysis and balance assessment. In some cases, additional tests may be required.

How is Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy treated?
Once Diabetic Neuropathy has been detected, the first step is to prevent further nerve damage by bringing blood sugar levels to within normal range, using dietary modifications, physical activity, diabetic medications and regular blood sugar monitoring.
Where Peripheral Neuropathy is causing painful symptoms such as stabbing, burning and tingling, other medications may also be prescribed.
What should I do if I have Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy?
If you have Diabetes, you play a vital role in minimising your risk of developing Peripheral Neuropathy, or preventing its possible consequences.
Simple measures you can take to prevent the development and progression of Peripheral Neuropathy are:
- keep your blood sugar levels within normal range to protect the nerves throughout your body
- keep your blood fat levels well controlled – a recent study found high levels of the fat triglyceride in the blood correlated with progression of Diabetic Neuropathy
- Footcare is also critical if you have Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Simple measures you can take to care for your feet are
- wear well-fitting protective shoes and socks to avoid injuring the skin on your feet
- see your Podiatrist if you have callus or corns under your feet – callus is a risk factor for ulceration in people with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
- inspect your feet daily for injuries, and if you notice any cuts, wounds, blisters, malodour, redness or swelling see your Podiatrist as soon as possible to prevent any problems from worsening.
Our podiatrists in Brisbane Northside are experienced in high risk foot care, amputation prevention and diabetes education. Please contact us to arrange an assessment.