What is diabetes?
Diabetes, or diabetes mellitus, is a metabolic disorder in which the production or performance of insulin in the body becomes impaired. about type 2 diabetes
Insulin is a hormone that causes the cells in the liver, muscle and fat tissue to take up sugar from the blood and store it as energy. If the body does not produce enough insulin, or its cells fail to respond to the insulin it produces, the glucose stays in the blood, resulting in high blood sugar levels.
The metabolic changes caused by high levels of sugar in your blood can lead to serious health problems affecting your cardiovascular system, your nervous system, your eyes, your teeth, your kidneys and your feet.

What are the different types of Diabetes?
There are 3 main types of diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, and occurs when the pancreas is unable to produce insulin. The cause of type 1 diabetes remains unknown, but we do know that it is not caused by eating too much sugar. Approximately 10 per cent of people with diabetes have type 1 diabetes. To date it remains unpreventable, and is always treated with insulin.
- Type 2 Diabetes is the most common type of diabetes, and usually develops in adulthood. It occurs when sugar builds up in your blood instead of being stored and used as energy, either because your body does not produce enough insulin, or its cells fail to respond to the insulin it produces. Type 2 diabetes is usually the result of a combination of lifestyle and genetic factors.
- Gestational Diabetes occurs during pregnancy, when your body cannot produce enough insulin to handle the effects of your growing baby and changing hormone levels, causing your blood sugar levels to rise. Once your baby is born, your blood glucose levels usually return to normal and you no longer have gestational diabetes. However, you remain at greater risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future.
What is pre-diabetes?
Some people may have blood sugar readings that are too high to be normal, but are not yet high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes. This result is known as ‘pre-diabetes’. Pre-diabetes is also referred to as ‘impaired glucose tolerance’ or ‘impaired fasting glucose’.
If you have pre-diabetes you are at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes. A diagnosis of pre-diabetes should be taken both as a warning, and as an opportunity to make positive lifestyle changes to prevent the development of type 2 diabetes.
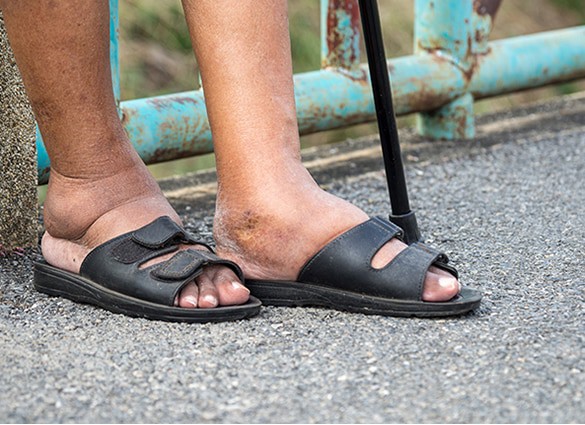

What are the signs and symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes?
The symptoms of type 2 diabetes develop so gradually that many people have diabetes long before they realise it. Some people have no symptoms at all, but when symptoms are present they can include:
- unusual thirst
- frequent urination
- weight change (gain or loss)
- fatigue or lack of energy
- blurred vision
- frequent or recurring infections eg tinea, thrush
- cuts and bruises that are slow to heal
- tingling or numbness in the hands or feet
- in men, difficulty getting or sustaining an erection
How is Type 2 Diabetes treated?
The cornerstone treatment for type 2 diabetes is regular physical activity and healthy eating. It is not necessary to reach your ideal body weight, as a loss of even 5-10kg can make a significant difference to your blood sugar levels.
- If you have high blood pressure or abnormal cholesterol your doctor will also treat these.
- If you smoke, you may need help or counseling to quit smoking.
- If healthy eating and regular exercise do not control your blood sugar levels, your doctor may need to prescribe tablets and possibly insulin to treat your diabetes.
- For most people, however, becoming more physically active and losing some weight will delay the need for tablets and insulin for many years.
What are the complications of Type 2 Diabetes if not adequately treated?
Common complications that occur in people with type 2 diabetes are:
- Cardiovascular disease: people with diabetes are three to four times more likely to develop heart and blood vessel problems, resulting in heart attack or stroke
- Atherosclerosis: people with diabetes have up to a six-fold increase in blockages of the blood vessels supplying blood to the heart and brain, and the arteries supplying blood to the legs and feet
- Neuropathy, or nerve damage which results in numbness, pins and needles, and altered sensation in the feet and hands
- Erectile Dysfunction in males
- Gastroparesis, also known as delayed gastric emptying, which occurs when diabetes damages the nerves that supply the muscles of the stomach
- Eye problems such as diabetic retinopathy, or damage to the light-sensitive area of the eye, and an increased risk of cataract and glaucoma
- Oral health problems such as periodontal disease, mouth ulcers and taste disturbances
- Kidney Disease: people with diabetes are three times more likely to suffer kidney failure, with diabetes the major cause of kidney disease in Australia.
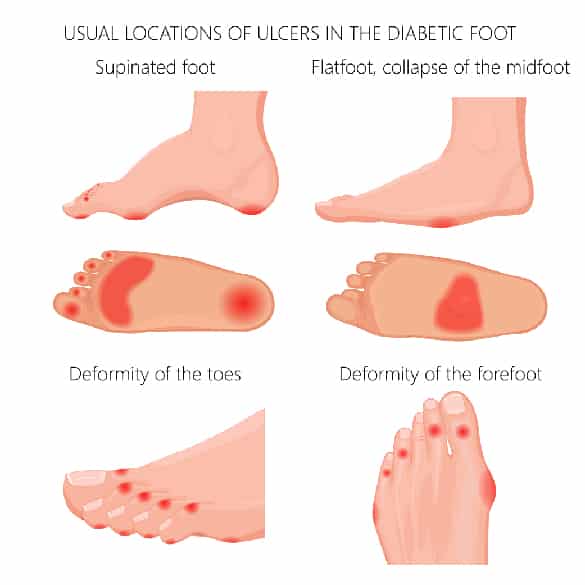
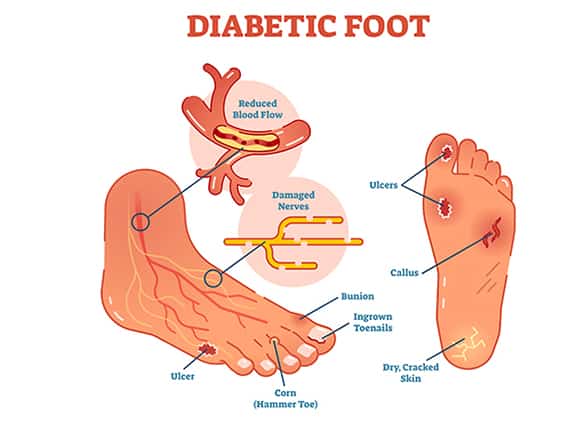
What are the complications of Type 2 Diabetes for my feet?
The complications of type 2 diabetes for your feet include:
- peripheral arterial disease (PAD), leading to insufficient blood flow to your feet and legs
- peripheral neuropathy, or damage to the nerves in your feet and legs
- an increased risk of injury to your feet as a result of both PAD and peripheral neuropathy
- foot ulcers as a result of impairment to your ability to recover from foot injuries
- infection, gangrene and amputation as a result of foot ulcers
- charcot foot syndrome, a deformity resulting from diabetic peripheral neuropathy
How do I know if I am at risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes?
Anyone can develop type 2 diabetes, but your risk is significantly increased if you:
- have a family history of diabetes
- are older than 55 years of age
- are overweight
- have high blood pressure or heart disease
- had gestational diabetes when you were pregnant
- are from an Aboriginal or Torres Strait Island, Chinese, Indian, Maori or Pacific Island background and are older than 35 years of age.
You can assess your risk of developing type 2 diabetes using the Diabetes Risk Calculator developed by the Baker IDI Heart & Diabetes Institute.
What should I do if I have Type 2 Diabetes?
If you have type 2 diabetes, your risk of developing diabetic complications is dependent on a number of factors, including:
- persistently high blood sugar levelsthe duration of your diabetes;smoking;
- high blood pressure
- high cholesterol and triglycerides
- genetic predisposition.
The good news is that you will significantly reduce your risk of developing complications with healthy eating, regular physical activity and well-controlled blood sugar levels, blood pressure and cholesterol.
You should also do everything you can to stop smoking. Contact the Queensland Health Quitline for help.
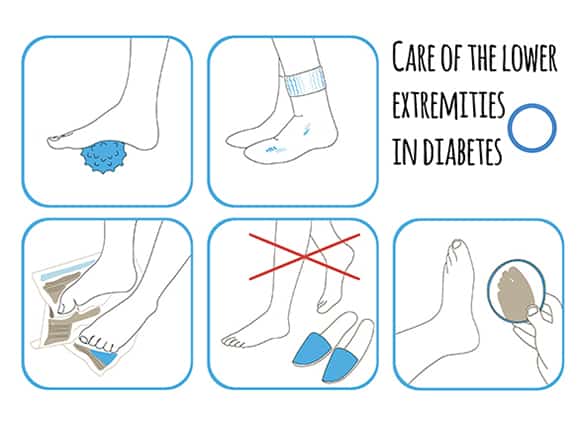
You can also reduce your risk of developing foot complications by seeing your podiatrist for a foot assessment at least once a year. Contact us to arrange a diabetic foot assessment as soon as possible.
You can find more information about type 2 diabetes at the following sites:
How is Type 2 Diabetes diagnosed?
Type 2 diabetes is diagnosed using a simple blood test ordered by your doctor. The most common blood test used to diagnose type 2 diabetes is the fasting blood glucose test, which measures the levels of sugar in your blood after you have fasted for 12 hours.


